Protocol-IP-197 Multi-Protocol Engine with Classifier, Inline and Look-Aside, 10-100 Gbps
Home > Security IP > Protocol Engines > Protocol-IP-197
The Protocol-IP-197 Multi-Protocol Engine is an IP family for accelerating IPSec, SSL, TLS, DTLS (CAPWAP), 3GPP and MACsec up to 5, 10, 20, 40, 50 and 100 Gbps in multi-core server, communication or network processors offering a large selection of cipher algorithms. Designed for fast integration, maximum CPU offload and offering full transforms, it provides a reliable and effective embedded IP solution that is easy to integrate into multi-core servers, communication and network processors. It is pre-integrated with the DPDK, Linaro ODP and Linux crypto APIs. Therefore, this IP is designed for seamless integration of network security processing in systems, with its inline and AMBA bus interfaces, embedded classification as well as support of the public APIs.
How the Protocol-IP-197 Multi-Protocol Engine works
The Protocol-IP-197 Multi-Protocol Engine is a protocol-aware packet engine comprised of an in-line streaming interface, a look-aside bus interface, an IPsec classifier, a packet transform engine and an optional post decryption processor. The packet engine is used as a bus master in the data plane of the system and processes packets with very little CPU intervention. This engine supports an AXI streaming interface, an AMBA (AXI, AHB, TCM) SoC bus interface and can be delivered in different configurations to support multiple performance grades from 10-100 Gbps, and cascadable up to 200 Gbps. Compared to the other Multi-Protocol engines it offers higher performance, in-line bump in the wire and bump in the stack systems, and it is able to handle extreme read latencies without performance loss. It has a variety of interfaces to cover many different use cases and integration options tailored to all the supported protocols. Due to the virtualization, the Protocol-IP-196 also allows separation of security parameters and keys from the different CPUs and secure applications in the system.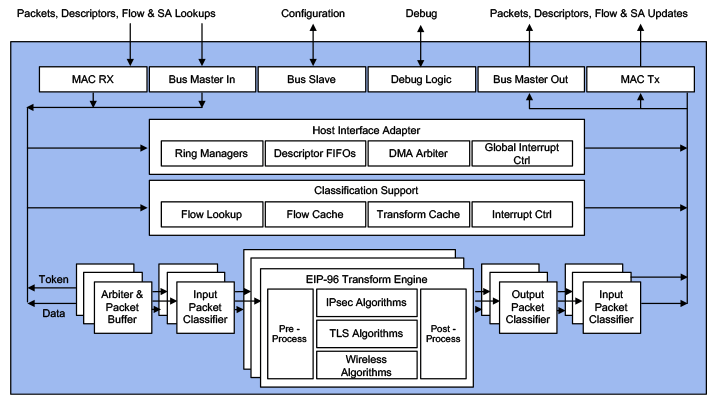
The Protocol-IP-197 is designed for systems requiring security protocol processing at extreme speeds, where CPU (farms) cannot handle the cryptographic workload due to performance or power limitations. The packet engine handles the security protocol operations and reduces power in high-end servers, communication and network processors for: network processors used in switch applications; data center processing and cloud computing; communication and high-end security gateways.
Multiple configurations are available to support larger data rates for specific use cases.
Secure Networking Basics: MACsec, IPsec, and SSL/TLS/DTLS

The MACsec, IPsec and SSL/TLS/DTLS protocols are the primary means of securing data in motion (communicated between connected devices). These protocols can be anchored in hardware or implemented in software as part of an end-to-end security architecture. This white paper provides fundamental information on each of these protocols including their interrelationships and use cases.
Features and Benefits
Key benefits:
- Silicon-proven implementation
- Fast and easy to integrate into SoCs
- Flexible layered design
- Complete range of configurations
- World-class technical support
- Driver development kit
- Full virtualization, key separation at application and CPU level
- Embedded cache
- AMBA interfaces
- NIST SP800-90A compliant DRGB
IPsec classification:
- IPsec-ESP header parsing to look-up a flow
- Fetch flow and corresponding transform record based on lookup result
- Update flow statistics
- Update transform statistics
- Support for IPv4 and IPv6
IPsec transformation (IPv4 and IPv6):
- Full IPsec packet ESP/AH transforms according to latest RFCs (2403, 2404, 2405, 2410, 3566, 3602, 3686, 4106, 4301, 4303, 4304, 4308, 4309, 4543, 4835, 4868, 4869, 6054,6379, 7321, 7539, 7634 and 8221)
- IPsec ESP and AH tunnel & transport mode
- Autonomous IPsec ESP packet classification and security association selection (both inbound and outbound)
- Insert ESP/AH header for outbound packets, strip and verify ESP/AH header for inbound packets
- Full sequence number processing, including ESN and full anti-replay check with various mask sizes
- Calculate and insert integrity check value for outbound packets, strip and verify for inbound packets
- Append (outbound) / strip and verify (inbound) padding up to 255 bytes
SSL3.0 / TLS1.0 / TSL1.1 / TLS1.2 / TLS1.3 / DTLS1.0 / DTLS1.2:
- Full single pass packet transforms according to latest RFCs (246, 4346, 4347, 5246, 6101 and 6347)
- Full Header processing:
- Insert header for outbound packets
- Strip and verify header for inbound packets
- Anti-replay check
- Trailer processing:
- Insert padding up to 255 bytes for outbound packets
- Strip and verify padding up to 255 bytes for inbound packets
- Calculate and insert Message Authentication Code for outbound packets, strip and verify for inbound packets
MACsec
- MACsec frame transforms according to IEEE 802.1AE standards
- SecTAG insertion and removal,
- PN insertion, removal and verification
- ICV generation, insertion, removal and verification
3GPP Wireless Algorithms
SA -Manager
- SA and flow record cache [bullet inserted]
- Optimized Security Association format
- Supports unlimited number of Security Associations
The cryptographic engine supports the following cryptographic algorithms:
- (3)DES in ECB and CBC with (3x) 56-bit key
- AES in ECB, CBC, ICM, CTR mode with 128/192/256-bit keys, GCM, GMAC and CCM modes, optional AES-XTS
- Optional ChaCha20, SM4, ARIA [bullet inserted]
- Optional ARC4 in Stateful and Stateless mode, up to 128-bit key
- Kasumi in basic and f8 mode (UEA1)
- SNOW3G in basic and 128-EEA1 mode (UEA2)
- ZUC in basic and 128-EEA3 mode (UEA3)
The hash engine supports the following algorithms:
- SHA-1, SHA-2-224/256, MD5
- Optional SHA-2-384/512, SHA-3 224/256/384/512 [bullet inserted]
- HMAC transforms for SHA-1, SHA-2, MD5
- Optional SM3, Poly1305 [bullet inserted]
- SSL-MAC transforms for SHA-1, MD5
- AES-CCM, AES-XCBC-MAC, AES-CBC-MAC-PRF
- GHASH, GCM, AES-GCM and AES-GMAC
- CRC32
- Kasumi in f9 mode (UIA1)
- SNOW3G in basic and 128-EIA1 mode (UIA2)
- ZUC in basic and 128-EIA3 mode (UIA3)
The Pseudo Random Number Generator supports:
- ANSI X9.31 compliant; based on the AES cipher
- Automatic IV generation
The Host interface with DMA controller supports:
- Multiple Descriptor Rings with individual access for multiprocessor support
- Scatter/Gather processing
- Automatic arbitration and bus flow control
- Supports big and little endian host systems
- Decouples Packet Engine from system bus interface
Inline interface:
- Ability to provide packets directly from the line interface into the Protocol-IP-197
- The packet engine autonomously performs full L3 transformation, including classification and IP header modifications and complete IPsec transformations
Master and slave interface:
- Master/Slave interface: AXI/AXI or AXI/APB or AHB/AHB slave interface
- Input and output buffers decouple Packet Engine from system bus interface
- Convenient SW debug interface including halt mode
- Clock switching interface for low power consumption
- Virtualization



