RT-130 Root of Trust
Foundational security in SoCs and FPGAs for IoT servers, gateways, edge devices and sensors
Home > Security IP > Root of Trust Solutions > RT-130
Designed to be integrated in power and space-constrained SoCs or FPGAs, the RT-130 Root of Trust (formerly VaultIP) is a SESIP, PSA Certified, and FIPS 140-3 compliant hardware core that guards the most sensitive assets on chips and establishes the foundation for platform security.
Featuring a firmware-controlled architecture with dedicated secure memories, the RT-130 hardware Root of Trust provides a variety of cryptographic accelerators including AES, SHA-2, RSA and ECC. Ideal for power and space-sensitive applications like IoT servers, gateways and edge devices, the RT-130 Root of Trust offers the best balance of size and performance available on the market.
The RT-130 offers a series of key security use cases ‘out of the box’, including:
- Secure Boot assist to host CPU(s) and protection of key material
- Secure firmware upgrade management for Host CPU
- Lifecycle management support
- Secure Debug support
- Secure device authentication and identity protection
The RT-130 provides a secure asset store:
- Only the RT-130 can manage, use and access the assets
- The O/S and applications cannot access key values
- Applications request asset use by reference
- Enforces policies for access and use of keys and cryptographic functions
- Key generation, derivation, storage and transport

Security in the ARM Ecosystem
Building security in an SoC aiming to meet the goals set by the ARM Platform Security Architecture (PSA) is a complex matter. This is compounded by the complexity of modern-day SoCs comprising multiple processors, security domains and security levels. The Rambus root of trust provides a solid foundation for the SoC security architecture ticking ‘all the boxes’ for reaching the security goals, while offering extensive support for effective integration into a complex TrustZone-based SoC infrastructure.How the Root of Trust Works
The RT-130 Root of Trust is a silicon IP core developed to protect an SoC platform and its operation. It allows the SoC to boot securely and protects sensitive key material and assets. At its heart, its Secure Asset Store allows import, negotiation, and creation of secret and private key material. Safe use of key material is enforced through a flexible key use and access policy. Keys can be securely stored in off-chip NVM. Fully featured, its cryptographic data plane associated to its DMA offloads the main CPU while never exposing secret data to the OS or the applications. It is designed to provide secure, energy efficient and accelerated security functions.
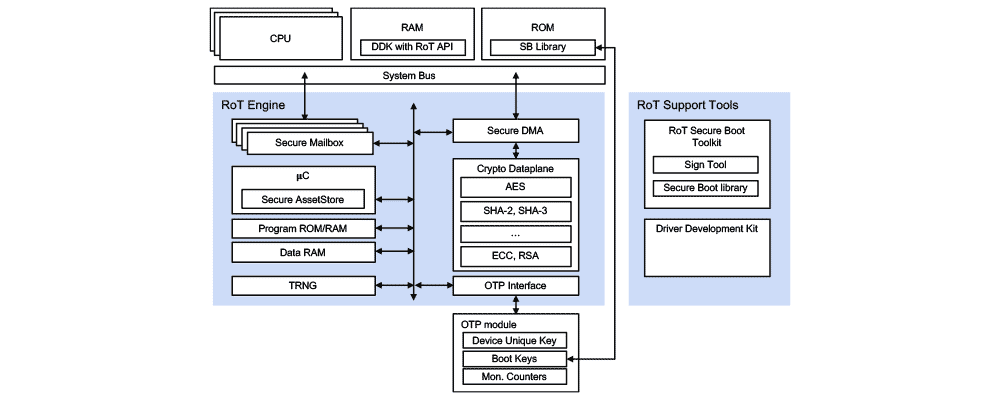
Readily deployable, the RT-130 Root of Trust is offered in off-the-shelf configurations, allowing a choice tailored to the needs of your application. Configurations differ by cryptographic accelerators contained and 3rd-party certification and standard compliance.
The RT-130 is part of the broad Rambus Root of Trust portfolio, which ranges from small, lightweight cores designed to protect IoT endpoints all the way to fully programmable Root of Trust cores designed to protect the most sensitive government/defense chips and automotive deployments requiring ISO-26262 certifications.
Rambus can optionally offer dedicated certification support packages to its RT-130 licensees that provide related certification documentation, test scripts, and dedicated support to achieve FIPS 140-3, SESIP and PSA certification when embedded in your SoC or ASIC.

“Relying on Rambus for mission-critical security IP allows us to offer customers world leading document solutions and ensure their data is protected”
- Michihiro Okada, Deputy Senior General Manager, Corporate R&D Division at Kyocera
Solution Offerings
| Feature | Description | Details |
| SESIP | Certified Level 2 | SESIP Profile for PSA Certified RoT Component Level 2 version 1.0 REL 02 |
| PSA | Certified Level 2 RoT Component | |
| FIPS 140-3 | CAVP and CMVP Compliant | Includes CAVP certificates for NIST approved algorithms and ESV certified TRNG |
| FIPS 140-2 | CAVP and CMVP Certified | Includes CAVP certificates for NIST approved algorithms and ESV certified TRNG |
| Cipher Algorithm support | AES (all key sizes) Optional: ChaCha20, ARIA | Modes: CBC, CTR, CCM, CMAC, GCM, XTS ARIA Modes: CBC, CTR, CMAC, CCM, GCM |
| Hash Algorithms | SHA-1, SHA-2 Optional: SHA-3 | SHA-2 224-256-384-512 SHA-3 224-256-384-512 |
| Message Authentication Code Algorithms | HMAC-SHA-1, HMAC-SHA-2 Optional: HMAC-SHA3 | SHA-2 224-256-384-512 SHA-3 224-256-384-512 |
| AEAD Algorithms | AES-GCM, AES-GMAC, AES-CCM Optional: ChaCha20/Poly1305, ARIA-CCM | Modes: GCM, GMAC, CCM |
| Signature Generation and Verification | ECDSA EdDSA RSA up to 3096 bits | NIST P-224, P-256, P-384, P-521 Ed25519 |
| Key Agreement Algorithms | ECDH DH EdDH | NIST P-224, P-256, P-384, P-521 Up to 3096 bits Curve25519 |
| Key Transport Algorithms | ECIES RSA Wrap/Unwrap (RSA-OAEP) AES-WRAP | 128- and 256-bit strength Up to 3096 bits 128- and 256-bit strength |
| Random Number Generator HW | NIST SP800-90 compliant TRNG | NIST ESV certificate |
| Crypto Performance | Cipher/Hash Performance (Gbps) @500MHz | Scalable, ~2 Gbps |
| I/O Bus | AMBA Bus Master/Slave | AXI/AHB Master, AXI/AHB/APB Slave |
| OTP Interface | Interface to 3rd-Party OTP | TCM |
- Cloud-connected devices
- IoT (Internet of Things) devices
- Industrial IoT
- Sensors
- Gateways
Full Disk Encryption of Solid State Drives and Root of Trust
File encryption, file system encryption and full disk encryption (FDE) are methods offered by the industry to allow users to protect their data stored on non-volatile storage devices, such as Solid State Disks (SSD). The main feature of FDE is to protect stored system and user date from unauthorized reading, writing, alteration, moving or rolling back. However, extended security features are key to securing FDE implementation.



