Taking a closer look: The Rambus CMRT
The recent Meltdown and Spectre vulnerabilities illustrate the critical need for a new generation of devices that execute sensitive security functions in a secure core which is physically separated from the primary CPU. This is precisely why Rambus is launching its CryptoManager Root of Trust, a fully programmable hardware security core built around a custom RISC-V CPU.
Siloed from the primary processor, it is specifically designed to securely run sensitive code, processes and algorithms.
In addition to the CPU, the Rambus CMRT contains a large set of hardware blocks arranged around an internal bus fabric.
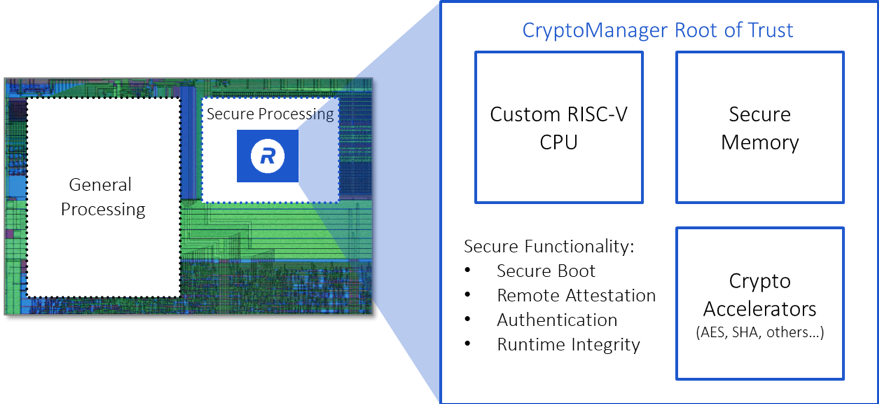
The Rambus CMRT provides the primary processor with a full suite of security services, such as secure boot and runtime integrity checking, remote attestation and hardware acceleration for symmetric and asymmetric cryptographic algorithms. Access to cryptographic accelerators, keys, memory ranges and I/O pins is restricted and enforced on a hardware level. Similarly, critical operations, such as key derivation and key unwrap, are performed by – and in – hardware.
Protecting against a wide range of attacks
The Rambus CMRT core utilizes advanced anti-tamper techniques to provide the highest level of security and protection against a wide range of attacks, such as fault injection. These include logic and crypto redundancy, secure state encoding and ephemeral keys that are generated on-the-fly from multiple splits and flushed immediately after use. In addition, the CMRT core features an optional Entropic Array with a proprietary logic structure that provides robust protection against emulation and reverse engineering. The CMRT core also helps protect against:
- Host processor compromise
- Non-volatile memory (NVM) key extraction, tearing and other attacks against NVM writes
- Corruption of non-volatile memory or fuses
- Test and debug interface attacks
- Power/EM analysis (SPA/DPA) and other side-channel attacks, including timing attacks
- Manufacturing/personalization facility compromise (insider attack)
- Man-in-the-middle and replay attacks
- Probing of external buses
Targeting multiple verticals and applications
According to Bret Sewell, SVP and general manager of the Rambus Security Division, the versatile CMRT is targeted at multiple verticals, including the Internet of Things (IoT), the automotive space, connectivity and sensors.
“The fundamental pillars of architectural design freedom – secure processing siloed away from general processing and layered security with multiple roots of trust – are unique to the CMRT design and facilitate easy implementation with the highest levels of protection,” he states. “The CMRT also embeds features that allow semiconductor manufacturers and device OEMs to insert hardware keys and enables IoT service providers to manage IoT endpoints throughout their lifecycle in the field.”
By establishing the trust chain early in the silicon manufacturing process, says Sewell, a security core can enable trusted provisioning and robust auditing of security-related activity throughout all phases of the chip lifecycle.
“The CryptoManager Root of Trust creates a secure foundation for Rambus’ comprehensive CryptoManager suite of solutions, which also includes the CryptoManager Provisioning Infrastructure and CryptoManager IoT Security Service,” he adds.
Establishing trust at the hardware level is “critical”
Commenting on Rambus’ launch of its CryptoManager Root of Trust (CMRT), IDC research director for IoT Security Abhi Dugar notes that the semiconductor industry faced some of its most significant security challenges during 2018.
“The potential to encounter additional security flaws will not go away any time soon as more IoT devices enter the market,” he elaborates. “To address existing and new threats, establishing trust at the hardware level will be critical – and a secure, siloed core can help ensure that this new generation of devices can be protected from security flaws.”
Putting security first with an embedded secure core
Rick O’Connor, the executive director of the RISC-V Foundation, expresses similar sentiments.
“The Meltdown and Spectre flaws revealed a new class of vulnerabilities as common processors employ acceleration techniques like speculative execution to improve processing performance,” he states. “With solutions like the Rambus CryptoManager Root of Trust, the extensible RISC-V ISA enables developers to build connected products with a fundamentally more robust approach to security.”
CMRT: Additional benefits and features
Additional key CryptoManager Root of Trust benefits and features include:
Design Freedom: The open RISC-V instruction set architecture (ISA) allowed Rambus to design a custom processor without microarchitecture constraints, enabling a security first design. The CryptoManager Root of Trust is purpose-built to be safe and independent from general processing, offering a smaller and simpler approach without sacrificing security. This provides customers with the opportunity to better design and validate their products.
Siloed: The CryptoManager Root of Trust is a fully user-programmable processor specifically designed for security use and physically separated from the primary processor with dedicated secure memory. Siloing allows the hardware Root of Trust to function in a known secure state, without allowing unintended access to secure functions through software backdoors.
Layered Security: The root of trust is designed with multiple security layers. A small, ultra-secure nucleus builds outwards to less secure sections. The less secure sections can only access higher levels of security with hardware-based permissions. The Rambus CryptoManager Root of Trust supports multiple roots of trust and enables various parties to use the core without exposing keys.
Conclusion
Meltdown and Spectre illustrate the critical need for a new generation of devices that execute sensitive security functions in a secure core which is physically separated from the primary CPU. Built around a custom RISC-V CPU, the CryptoManager Root of Trust (CMRT) is at the forefront of a new category of programmable hardware-based security cores. Siloed from the primary processor, it is specifically designed to securely run sensitive code, processes and algorithms.
Indeed, the Rambus CMRT provides the primary processor with a full suite of security services, such as secure boot and runtime integrity, remote attestation and broad crypto acceleration for symmetric and asymmetric algorithms. Targeted at multiple verticals, the versatile CMRT creates a secure foundation for our comprehensive CryptoManager suite, which also includes the CryptoManager Provisioning Infrastructure and CryptoManager IoT Security Service. Put simply, Rambus’ CryptoManager solution spans silicon to services, beginning with the chip manufacturing process and continuing throughout the device lifecycle.


Leave a Reply