HMAC-IP-59 MD5, SHA-1, SHA-2, SHA-3 Hash based HMAC, accelerators
Home > Security IP > Crypto Accelerator Cores > HMAC-IP-59
HMAC-IP-59 (EIP-59) is IP for accelerating the various single pass HMAC (FIPS-198-1) algorithms using secure hash integrity algorithms like MD5 (RFC1231), SHA-1 (FIPS-180-2), SHA-2 (FIPS-180-3/4) and SHA-3 (FIPS-202), up to 8 Gbps. Designed for fast integration, low gate count and full transforms, the HMAC-IP-59 accelerators provide a reliable and cost-effective embedded IP solution that is easy to integrate into high-speed crypto pipelines.
Secure Hash-based HMAC family of accelerators
Available in several configurations / performance grades
Library element for platform security and packet engines
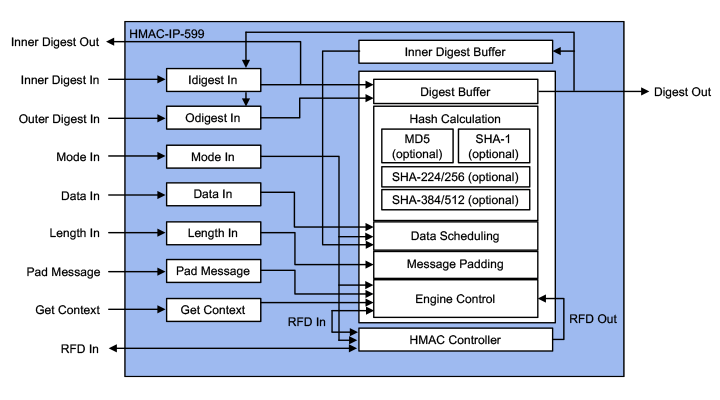
How the HMAC-IP-59 works
The HMAC-IP-59 is a family of the cryptographic library elements in the Rambus hardware IP library (formerly of Inside Secure). For example, the HMAC-IP-59 is the hash core embedded in the IPsec packet engines as well as the VaultIP root of trust cores providing support for MD5 and SHA based Hash and HMAC functions. The accelerators include I/O registers, encryption and decryption cores, and the logic for feedback modes and key scheduling.
Sustained performance for any object sizes ranges from 2 to 8 Gbps, depending on the configuration and area. Gate counts ranges from 23K to 95K gates depending on the configuration.

Anti-Tampering Technologies
The design of chip anti-tamper protection needs to adapt and scale with rising threats. Adversaries range from high school hackers to well-funded state actors. Given the threats, it’s useful to think about anti-tamper countermeasures as a hierarchy of safeguards that parallel the type, effort and expense of attacks. Watch this webinar to learn the eleven kinds of tampering attacks and their required skills and resources, and countermeasures for each of these attacks.
HMAC-IP-59 Information
Key benefits:
- Silicon-proven implementation
- Fast and easy to integrate into SoCs
- Flexible layered design
- Complete range of configurations
- World-class technical support
Features:
- Wide bus interface
- Supporting HMAC and Basic Hash operations for all algorithms: MD5, SHA-1, SHA-2 (224, 256, 384, 512), SHA-3 (224, 256, 384, 512)
- MAC Key XOR and Message padding
- Message data scheduling hardware
- Calculation of “inner digest” and “outer digest” from a MAC Key input
- Calculation of “inner hash” and “outer hash” from a MAC Key input or “inner digest” and “outer digest” input
- MAC Key sizes shorter, equal and longer than algorithm block size
- Hash and HMAC context switching
- Continued hash / HMAC support
- Standard, high frequency and high performance versions available
- Secure hash standard-compliant FIPS-180-2, FIPS-180-3, FIPS-180-4
- HMAC support for all algorithms, compliant with FIPS-198-1, FIPS-198
- Fully synchronous design
Alternative:
- HASH-IP-57 / EIP-57 Hash MD5, SHA-1, SHA-2, SHA-3

Introduction to Side-Channel Attacks
Side-channel attacks conducted against electronic gear are relatively simple and inexpensive to execute. Such attacks include simple power analysis (SPA) and Differential Power Analysis (DPA). As all physical electronic systems routinely leak information, effective side-channel countermeasures should be implemented at the design stage to ensure protection of sensitive keys and data.



