Home > Memory Interface Chips > DDR5 DIMM Chipset
DDR5 Registering Clock Driver, Multiplexed Registering Clock Driver, Multiplexed Data Buffer, Power Management IC, SPD Hub and Temperature Sensor Chips
The Rambus DDR5 server memory interface chipset for RDIMMs, consisting of DDR5 Registering Clock Drivers (RCD), Power Management ICs (PMICs), Serial Presence Detect Hubs (SPD Hub) and Temperature Sensors (TS), is tailored for the high-capacity, high-bandwidth performance requirements of the latest generation DDR5 memory systems. Rambus also supports DDR5 server Multiplexed Rank DIMMs (MRDIMMs) with Multiplexed Registering Clock Drivers (MRCD), Multiplexed Data Buffers (MDBs), PMIC, SPD Hub and TS chips. In current and future RDIMMs and MRDIMMs, these chips enable server computing systems to handle the most demanding workloads and applications.
| Description | Part Number | Product Brief | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8000 MT/s Registering Clock Driver | RCD5-GXXX | Server RDIMM 8000 | |
| 7200 MT/s Registering Clock Driver | RCD4-GA0A | Server RDIMM 7200 | |
| 6400 MT/s Registering Clock Driver | RCD3-G1A | Server RDIMM 6400 | |
| 5600 MT/s Registering Clock Driver | RCD2-G1B | Server RDIMM 5600 | |
| 4800 MT/s Registering Clock Driver | RCD1-G1EX | Server RDIMM 4800 | |
| 12800 MT/s Multiplexed Registering Clock Driver | D5MRCD2GXX | Server MRDIMM 12800 | |
| 12800 MT/s Multiplexed Data Buffer | D5MDB2XGXX | Server MRDIMM 12800 | |
| PMIC5000 High Current Power Management IC | P1945XXGA1 | Server RDIMM 4800 – 7200 | |
| PMIC5010 Low Current Power Management IC | P1943XXGA0 | Server RDIMM 4800 – 7200 | |
| PMIC5020 Extreme Current Power Management IC | P1947XXGA1 | Server RDIMM 4800 – 7200, MRDIMM 8800 | |
| PMIC5030 Gen2 Server Power Management IC | Server RDIMM 8000, MRDIMM 12800 | ||
| SPD Hub with Internal Temperature Sensor | SPD5118-G1B | Server RDIMM, MRDIMM Client UDIMM, SODIMM, CSODIMM, CUDIMM | |
| Temperature Sensor | TS5110-G1B | Server RDIMM, MRDIMM |
Ask the Experts: Rambus DDR5 DIMM Chipset Performance
The Rambus DDR5 Memory Interface Chipset enables increased memory capacity, while maintaining peak performance on dual inline memory modules (DIMMs). These gains are essential to handle the most data-intensive workloads.
DDR5 Registering Clock Drivers (RCD), Power Management ICs (PMICs), Serial Presence Detect Hubs (SPD Hub) and Temperature Sensors (TS) are targeted for use in server DDR5 Registered DIMMs (RDIMMs) to deliver exceptional bandwidth, performance and capacity.
Data Center Evolution: DDR5 DIMMs Advance Server Performance

Driven by a confluence of megatrends, global data traffic is increasing at an exponential rate. For example, 5G networks are enabling billions of AI-powered IoT devices untethered from wired networks. Nowhere is the impact of all this growth being felt more intensely than in data centers. Indeed, hyperscale data centers have become the critical hubs of the global data network. DDR5 DRAM will enable the next generation of server systems providing the massive computing power of hyperscale and enterprise data centers. Learn about the benefits of DDR5 memory and the design considerations for implementing DDR5 DIMMs.
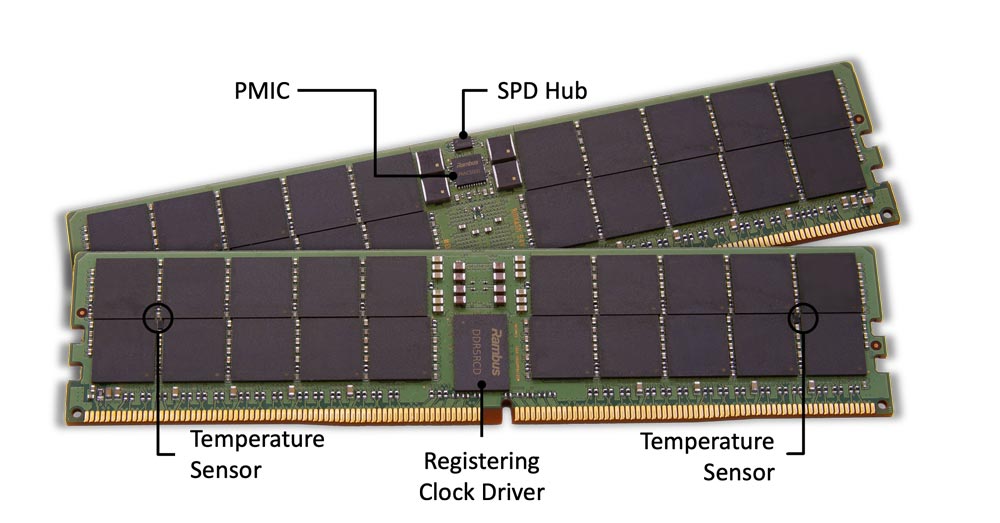
The RCD is the key control plane chip which distributes Command/Address signals and clock to the DRAM devices on the RDIMM.
The PMIC provides power management that scales with the number of memory modules needed by the system configuration.
The SPD Hub enables communication via the I3C bus of important data for system configuration and thermal management. It has an integrated temperature sensor.
Two TS per DIMM offer precision thermal sensing and, in combination with the SPD Hub, provide three points of thermal telemetry for the memory module.
Scaling DDR5 DIMMs
DDR5 DIMMs increase memory bandwidth and capacity over DDR4 DIMMs with new innovations and a new module architecture. While DDR4 DIMMs top out at 3200 MT/s, the first DDR5 DIMMs launched at 4800 MT/s, a 50% increase in memory bandwidth.
Given the voracious demands for greater memory bandwidth to support advanced workloads including HPC and AI/ML, DDR5 will continue to scale. Rambus is constantly advancing the performance of its DDR5 solutions to meet growing market needs. Rambus has led the push to higher performance levels most recently with the announcement of the industry’s first 8000 MT/s DDR5 RCD.
DDR5 FAQs
DDR5 memory delivers higher bandwidth and capacity compared to the previous DDR4 standard. DDR4 DIMMs top out at 3.2 GT/s, initial DDR5 DIMMs deliver a 50% bandwidth increase to 4.8 GT/s, and Rambus is already sampling 4th Gen 7.2 GT/s DDR5 RCDs. In addition, DDR5 DIMMs support up to 4X the capacity of DDR4 DIMMs: 256GB vs. 64GB for DIMMs using single-die package DRAM devices.
The SPD Hub is a chip on DDR5 DIMMs used for control plane communication between the DIMM and Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) on the motherboard. The SPD Hub has an integrated temperature sensor (TS), which in conjunction with the two discrete TS ICs in RDIMM modules, provides thermal telemetry data used as an input to system cooling management.
Rambus has over thirty years of high-performance memory experience delivering industry leading data rates and bandwidth performance. As DDR5 scales to higher speeds, maintaining signal and power integrity becomes more difficult, and the Rambus DDR5 chipset builds on the company’s memory and signaling expertise.



